From the inside view of mysap office work place you'll find a way to attain all information, purposes, and providers inside and out of doors your company. This can include SAP programs and non-SAP techniques, as effectively as the mySAP Marketplace or any other Web services. You may use your personal portal to your day by day work to access all applications you need, similar to Microsoft Outlook or mySAP Business Data Warehouse.
From the outside view you'll have the option to reach all relevant info you need, for instance, to work with your partner. That could embrace access to an SAP system or any other internal data that is related to the portal.Within the mySAP.com technique, SAP delivers the capacity for constructing a personalized enterprise portal by deploying the mySAP Workplace. This portal supplies access to all SAP features, in addition to the total range of Internet functions, providers, and communities. The mySAP.com portals are methods of accessing all the providers and advantages afforded by the mySAP.com strategy. The mySAP.com Office is tailored to people, companies, and industries.
It places the enterprise options, information, and services they need to reach their day by day enterprise actions at their fingertips. The customers, by their Web browsers, can access functionality that's most related to their roles after which configure their personal desktops to go nicely with their particular person work styles. As has been introduced in previous chapters, one of many mySAP.com targets as a full e-business solution is to offer the appropriate info, features, and purposes to staff in addition to to enterprise partners. mySAP Workplace gives a customizable and role-based mostly interface for their requirements.
- Entry to enterprise resolution applications, both SAP and non-SAP
- Entry to companies available on the Web
- Access to inner company data, reports, press releases
- Instant push information when logging on (MiniApps)
- Access to any user functions
- Access to SAP Markets and other Marketplaces

mySAP Workplace: Primary Features
The mySAP Workplace is the browser-based mostly environment through which the consumer can entry a set of business applications. This access is offered by a common and distinctive interface for all the features required by the users according to their roles, no matter on which platform, system, or utility the enterprise course of is run. With a objective to accomplish this objective, SAP has included unique options within the Workplace that, mixed, present the facility to change into the strategic interface for accessing different utility parts and business processes, including those which might be non-SAP. Some typical parts that can be discovered throughout the mySAP.com technique are:
KW (Information Warehouse), BW (Enterprise Information Warehouse), CRM (Buyer Relationship Administration), BBP (Business to Enterprise Procurement), and APO (Advanced Planner and Optimizer).
The Office’s most important features are:
- Internet browser access to all business functions
- Role-based consumer menu, security, and software access
- SSO (Single Sign-On) for accessing all functions with just one authentication course of
- MiniApps for providing on the spot and useful data in conserving with function
- Drag&Relate functions to simply integrate information and features amongst totally differentpurposes and Web services
- EnjoySAP user-friendly interface that can be tailored and customised by the user
- Standard and superior Web know-how
Office Architecture
Workplace Elements :
1. The LaunchPad on the left facet, which reveals the customized function-based mostly menus and features for the user. This might be thought-about the pull space of the Office, that is, where customers make requests to business processes or services.
2. The WorkSpace on the suitable aspect accommodates both the MiniApps (additionally referred to as the House Page) or the business transactions or services as required by the menus and functions. The House Page (MiniApps) can be thought-about the push area because it proactively sends information to the person routinely as programmed.
The preliminary entry or login to the Workplace is completed via a URL (Uniform Useful resource Locator) request to the Workplace server, which will be accessed using a predefined link to the URL or by typing it immediately within the browser. An example of URL request to the Office server is:
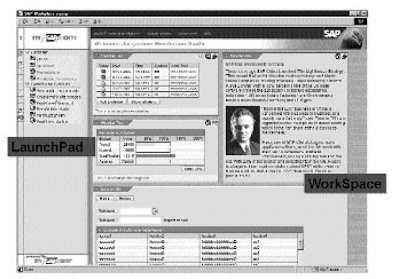
The LaunchPad is personalised based mostly on the user role that connects to the Workplace. It accommodates particular activities that are related for the person’s job position. It can include the enterprise functions of mySAP elements, in addition to non-SAP methods, functions, and providers, as long as they are often known as or referenced by a URL.
The LaunchPad can include a quantity of roles for each user. It additionally permits the customization or personalization of some parts. For example, the users can add their favourite Web hyperlinks or access their most regularly used paperwork or files. The Workspace can show the results of the MiniApps as they've been assigned to the person, in addition to the results of SAP transactions or business scenarios. The MiniApps offered by the Office are dependent on the user roles. Some examples of MiniApps include Internet hyperlinks, new mail, to-do lists, pending
orders, news, studies, alerts,Workflow gadgets, and so on.Moreover, the Office includes the Drag&Relate performance, which is used for linking business objects from different transactions or applications and passing the values from one object to another. There are completely different scenarios for linking objects via the Drag&Relate technology.
Technical Background
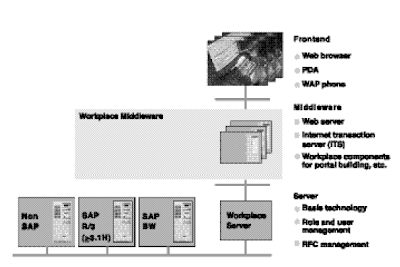
From a logical point of view, the Office architecture is based on three levels, or layers.
1. The shopper or browser put in on the person’s workstation or another machine that supports an Web browser. This component is used for communication with the Internet server. Presently, the one browser supported for working with the Office is Microsoft Web Explorer 5.zero or increased, but different options could be out there in the future. In addition to the browser, some functions would possibly require the set up of a unique GUI (like the normal SAPGUI for Windows, the Java GUI, or Citrix) as a result of the SAPGUI for HTML doesn't support some features. Transactions supported by different GUIs are outlined within the Office customizing desk TSTCCLASS.
2. Office Middleware. The Office Middleware is made up of a Web server and an ITS. The connection established from a Web browser should be in dialog with a Web server that is a half of the Office Middleware. The Net server communicates with the component systems or back-finish programs through the ITS. Each components make up the Office Middleware. If the Drag&Relate performance goes to be enabled, different parts shall be required, such as the SAP DCOM (Distributed Frequent Object Mannequin) and the Drag&Relate Servlets.
3. Back-finish programs that are integrated in the Workplace. The principle system that needs to be linked is the Workplace server, a special SAP system (based on the mySAP Foundation Middleware like R/3 launch 4.6). From there, users and roles are administered, as properly as the RFC (Distant Operate Calls) connections to other part systems. All supported systems that are accessed by means of the Office-akin to R/three, BW, KW, and so on-are normally often known as element systems.
Particular purposes or transactions that cannot be displayed, handled, or transformed into HTML format-in different phrases, that can only be executed utilizing SAPGUI for Home windows or SAPGUI for Java-are instantly displayed using their corresponding entrance-finish software components.
The Java SAPGUI is executed throughout the WorkSpace window and doesn't require additional software program, besides that the Java plug-ins should be provided from a server, normally from the same Internet server.When the transaction goes to be executed utilizing SAPGUI for Home windows, the system launches the SAPGUI within the WorkSpace of the browser window. In each cases of SAPGUI for Java and SAPGUI for Windows, the transactions (the process logic) are executed within the corresponding part system. There are some exceptions, though.For a consumer to access a Workplace, all that's needed is a workstation (usually a PC), Internet Explorer release 5.x or increased, and a valid username and password.
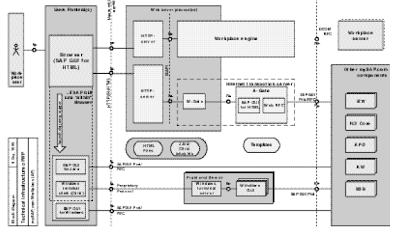
Workplace Server
The Office server itself is a SAP R/three 4.6 Foundation system. All platforms and databases supported by SAP are supported, as well. If you're using CUA, the Workplace server needs to be your CUA server, as a outcome of it's the central system that is aware of all users. The Office server is liable for consumer, position, and personalization management, in addition to content. The content material consists of information about the activities that might be reached from the LaunchPad and the MiniApps.
Workplace Middle ware
The Office Middleware consists of the Net server and the ITS with the Portal Builder Engine. If Drag&Relate or Terminal Services are used, the Drag&Relate Servlet and the Citrix Terminal Server belong to the Office Middleware as well. Determine 5-5 exhibits a greater view of the Workplace Middleware. The ITS makes use of so-referred to as HTML template information to generate the HTML files with the R/three data. The template files comprise placeholders and ITS directions within the SAP scripting language Business HTML.
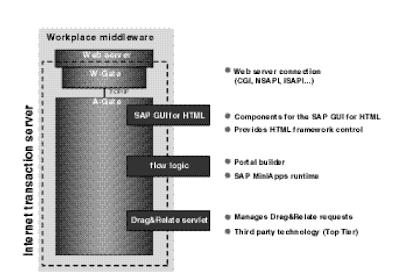
Opposite to Simple Web Transactions, functions developed with ITS stream logic solely use RFC and BAPI (business utility programming interface) calls to the R/three system and are often not based on a transaction in the R/3 system. Much like Straight forard Internet Transactions, HTML template information are used to outline the design of the application, but the flow of the application is decided with so-called movement files. Circulation files outline which screens are displayed and which RFCs and BAPIs are called. This state of affairs is often called Outside In.
The usual for R/3 purposes within the mySAP Workplace is the SAPGUI for HTML, typically called WebGui. The SAPGUI for HTML seems to be like a basic SAPGUI for Windows, however it's running in the Net browser and is predicated on HTML. Most of the transactions can be used in the SAPGUI for HTML without issues, however certain transactions require a SAPGUI for Home windows or a SAPGUI for Java. Figure 5-6 shows an example of the completely different GUIs. The fourth programming mannequin for the ITS, WebRFC, makes use of RFC calls to get HTML pages directly from the R/3 server. So the generating of the HTML pages takes place on the R/three software server and never on the ITS itself.
The Office Engine is a service, sapwp, working on the ITS occasion for the Workplace server. If the consumer logs in to the Workplace, the LaunchPad, WorkArea, Channels, and MiniApps are generated by the sapwp service. If a person clicks on an entry within the LaunchPad to begin an software on a Work place component system, he or she connects on to the ITS of the component system.The ITS service of the Office is simply not involved in this step.
Related Posts:
MySAP CRM architecture and E procurement introduction
MySAP CRM E procurement
MySAP CRM business intelligence at work
CRM data administration in mysap and business intelligence
sap internet transaction server introduction
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
No comments :
Post a Comment